Dr. Gawande, received the “Deans Award” from Dean of Palakcy University for the best publication output in the Chemistry Discipline.
13.12.2015

Gawande et al. review article, “Core-shell Nanomaterials: Synthesis and Applications in Catalysis and Electrocatalysis” Published in Chemical Society Reviews and selected for “Inside front cover”, 2015
26.04.2015
Core-shell nanoparticles (CSNs) are a class of nanostructured materials having interesting properties and a broad range of applications in catalysis, biology, materials chemistry and sensors. The main aim of this review to explored core-shell nanoparticles into various catalytic and electrocatalytic applications including oxidation, reduction, coupling reactions which utilized as sustainable solutions to resolve the energy crisis. Synthetic methods for preparation of different classes of CSNs, including the Stöber method, solvothermal method, one-pot synthetic method involving surfactants, etc. are briefly reviewed in this article.
This review TOC highlighted “Inside front cover” in chemical Society Reviews Journal.
Chemical Society Reviews, 2015, 44, 7540-7590. (IF- 40.44); Highly Cited Article
Web: http://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/articlelanding/2015/cs/c5cs00343a#!divAbstract

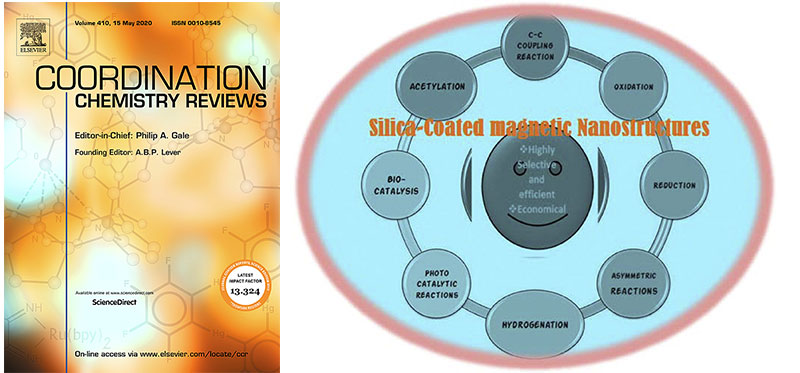
Gawande et al. article “Silica-decorated magnetic nanocomposites for catalytic applications” published in Co-ordination Chemistry Reviews, 2015.
14.01.2015
-Sustainable Chemistry is considered an attractive pathway because of its ability to improve chemical activities which avoid its undesirable side effects of toxic and hazardous chemicals. In heterocatalysis, nano-materials are suitable candidates for Green Chemistry catalysis due to their high efficiency, great stability, durability, and cost-effectiveness. Magnetic nanocatalyst is an important class of nanomaterial-based catalysts due to its easy separation and recovery after the organic transformations from the mother liquor. Herein Gawande et al. nicely reviewed synthesis, characterization and catalytic applications of silica-based magnetic nanomaterial supported catalysts as a nanocatalyst. The sustainable synthesis of magnetic nanoparticles (MNPs) using less toxic and readily available precursors, as well as environmentally benign solvents or supports, under ambient conditions are briefly described. Applications of silica-based magnetic nanomaterials in some challenging reactions, such as oxidation, carbon-carbon coupling reactions, olefin metathesis and photo- and bio-catalysis are thoroughly explained. This review is helpful for the researchers to design and preparation of well-defined heterogeneous catalysts with highly desirable properties also it gives an idea about the new generation of highly stable and selective catalysts in the future.
Co-ordination Chemistry Reviews, 2015, 288, 118-143. (IF- 13.32)
Web: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0010854515000041
Halluin et al. article entitled “Graphite-Supported Ultra-Small Copper Nanoparticles: Preparation, Characterization and Catalysis Applications” published in Carbon, 2015.
07.06.2015
Metallic nanoparticles (NPs) at the nanometer scale can act as a bridge between atomic and bulk metal, exhibiting unique physical, electronic and chemical properties. Halluin et al. reported synthesis of graphite-supported ultra-small copper nanoparticles (Cu NPs) under mild conditions by reduction of copper(II) acetate in MeOH at room temperature, under an atmosphere of hydrogen. Applications of designed heterogeneous catalysts are successfully evaluated for the copper-catalyzed arylation of pyrroles with aryl diazonium salts and the 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition of organic azides with phenylacetylene. This research provides significant insights for heterogeneous copper catalysts that should be of interest to synthetic chemists concerned by the metallic contamination of their products.
Carbon, 2015, 93, 974-983. (IF- 7.46)
Web: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0008622315005321

Rathi et al. review article entitled “Microwave-Assisted Synthesis- Catalytic Applications in Aqueous Media” published in Co-ordination Chemistry Reviews, 2015.
Microwave-assisted organic synthesis (MAOS) is one of the most powerful and sustainable tools in synthetic chemistry and it attracted much attention due to its outstanding properties like efficient atomic utilization, improved temperature regulation, reaction homogeneity, and possible modifications of activation parameters. In this review development of environmentally benign procedures for Microwave (MW)-assisted catalytic reactions performed in aqueous media are summarised. Also, catalytic MW-assisted methods used for the synthesis of a variety of heterocycles, cross-coupling reactions, C-H activation reactions, synthesis of peptides, urea’s, and carboxyl-containing coordination polymers and a host of miscellaneous reactions along with continuous flow capillary MW microreactors and other related flow applications nicely reviewed.
Co-ordination Chemistry Reviews, 2015, 291, 68–94. (IF- 13.32)
Web: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0010854515000314
Gawande and co-workers article entitled “Heterogeneously catalyzed strategies for the deconstruction of high-density polyethylene: plastic waste valorization to fuels” published in Green Chemistry, 2015.
The plastic industry generates enormous quantities of plastics with increasing rates (both production and consumption) which directly impacted on our environmental pollution in terms of plastic waste generation. High-density polyethylene (HDPE) makes a major contribution to municipal solid waste, which has a remarkable potential to be valorised into fuels (e.g. bio-oils). In this review, catalysts developed for the catalytic degradation of HDPE including metal oxides, sulphated metal oxides, zeolites, nanostructured zeolites, molecular sieves, fluid catalytic cracking (FCC) catalysts, metal carbonates and mesoporous materials for the production of chemicals and fuels (e.g. diesel and gasolines) are clearly described. Also, activities and selectivities, as well as important effects of additives, particle size, catalyst to polymer ratios and recent approaches for the waste management, very well summarised. The aim of review is to develop a novel method as well as a catalyst to process waste plastics to valuable products ie. “Waste to oil” including fuels and chemicals which contributed to environmentally sustainability and benign process development.
Green Chemistry, 2015, 17, 146-156. (IF- 9.7)
Web: https://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/articlehtml/2015/gc/c4gc01760a

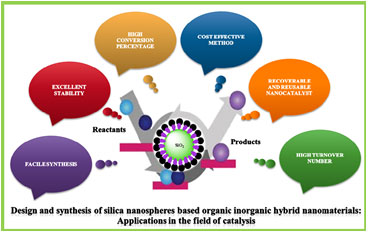
Sharma et al. review entitled “Silica-nanosphere-based organic-inorganic hybrid nanomaterials: synthesis, functionalization, and applications in catalysis” published in Green Chemistry, 2015.
09.04.2015
The design and development of organic-inorganic hybrid nanomaterials and their applications in catalysis is an important area in sustainable chemistry which opens various ways to develop environmentally friendly and benign catalytic processes for researchers. In this review synthesis and characterization techniques of silica nanoparticles (NP)-based organic-inorganic hybrid materials briefly described. Also, applications of silica-based nanoparticles in organic transformations such as addition, decomposition, condensation, polymerization, esterification, dehydrogenation, and amidation reaction nicely reviewed.
Green Chem., 2015, 17, 3207-3230. (IF- 9.7)
Web: https://pubs.rsc.org/–/content/articlelanding/2015/gc/c5gc00381d/unauth#!divAbstract